Internship
The purpose of the EP is to train a pediatrician who meets the requirements of the professional educational standard, who has the required amount of knowledge, skills and practical skills for independent diagnostic, therapeutic and preventive measures in the field of pediatrics in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine using advanced innovative technologies that are ready for continuous professional development.
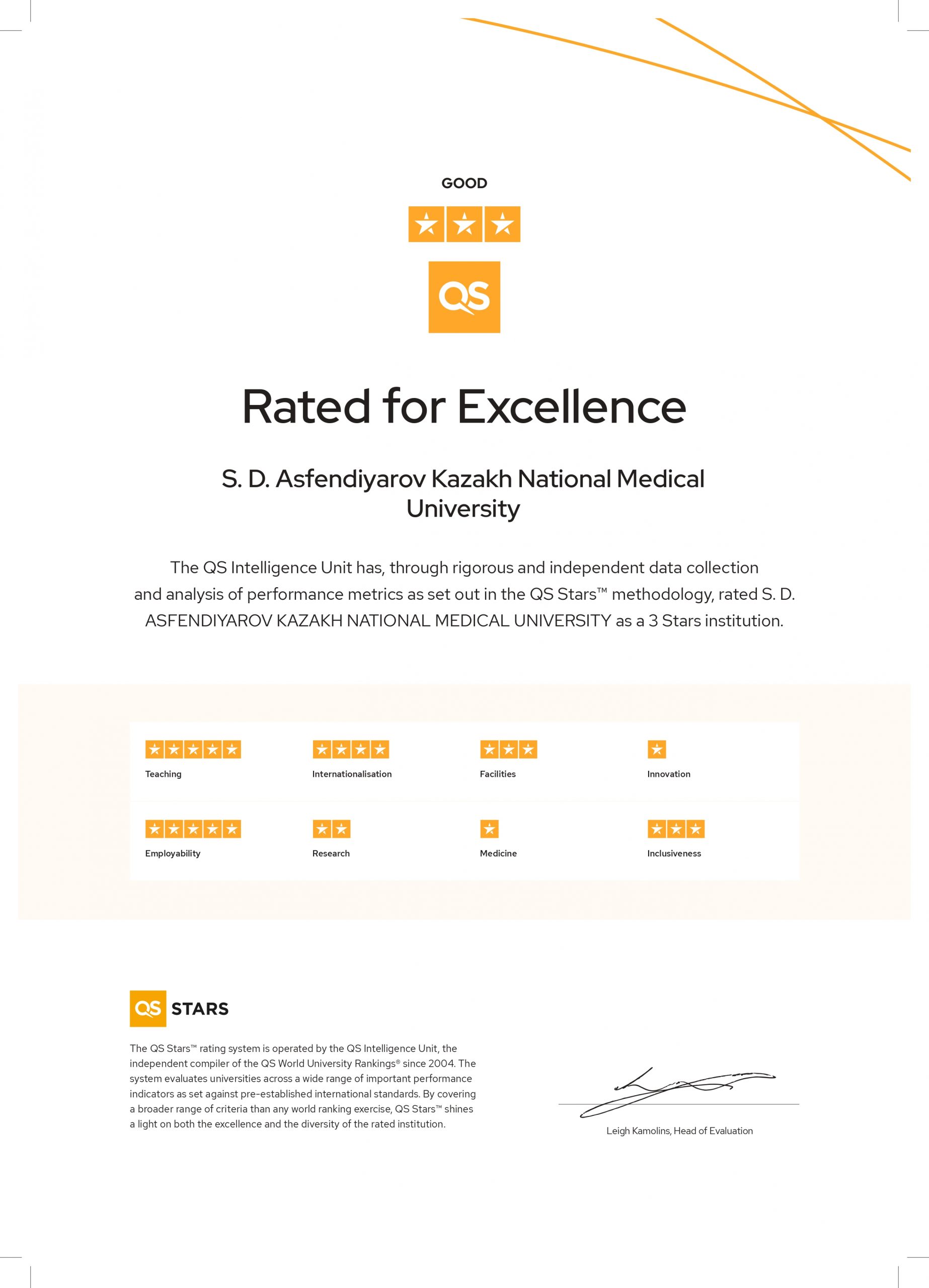
Mission of the educational program training of highly qualified and in-demand pediatricians with theoretical knowledge and practical skills for the effective performance of professional activities.
|
№ |
Program Learning Outcomes (LOs) The graduate will be able to: |
EER code |
|
1. |
Apply knowledge of clinical and biomedical sciences in providing quality patient-centered treatment. Conduct differential diagnosis and formulate a diagnosis taking into account modern classifications. |
ER1 |
|
2. |
Apply the skills of planning, conducting and analyzing clinical, laboratory and instrumental examinations for patients with the most common childhood diseases |
ER2 |
|
3. |
To select and evaluate safe, effective treatment in pediatric patients based on evidence-based medicine. Determine indications and provide qualified assistance in emergency and life-threatening conditions. |
ER3 |
|
4. |
Draw up and maintain medical accounting and reporting documentation, including in medical information systems. |
ER4 |
|
5. |
To carry out a set of screening and preventive measures for early intervention aimed at forming and strengthening the state of health of children, reducing morbidity and mortality. To carry out dispensary observation of pediatric patients in accordance with clinical protocols and standards of medical care. Rehabilitation measures. |
ER5 |
|
6. |
To act within the legal and organizational framework of the health care system of the Republic of Kazakhstan. |
ER6 |
|
7. |
Effectively interact with patients, their environment and work with colleagues as part of multidisciplinary teams to ensure an integrated approach to the treatment and prevention of diseases in patients |
ER7 |
|
8. |
Use scientific approaches, methods and principles of evidence-based medicine in their clinical practice and for continuous professional development. |
ER8 |
|
Profile disciplines |
|
|
Pediatric pulmonology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
Study of the organization of medical care for children in inpatient conditions. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, prevention of complications in children and adolescents with the most common respiratory diseases. Study of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases. Formation of knowledge and skills in laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of respiratory diseases in children and interpretation of the results obtained. |
|
Pediatric cardiology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
As part of the program, students will master the skills of early diagnosis of the most common diseases of the cardiovascular system in children, assessing the severity, predicting the course and prescribing timely pathogenetic therapy in order to reduce disability and improve the quality of life of patients. |
|
Pediatric rheumatology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
The discipline is aimed at studying the etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the most common rheumatic diseases in children and adolescents. It provides the formation of competencies necessary for further practical activities of a pediatrician and interaction with related specialists in a multidisciplinary team, knowledge of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment, the formation of knowledge and skills in methods laboratory and instrumental diagnostics and interpretation of the results obtained. |
|
Pediatric gastroenterology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
Study of the organization of medical care for children in inpatient conditions. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, prevention of complications in children and adolescents with the most common gastroenterological diseases. Study of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment. Formation of knowledge and skills in the methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics and interpretation of the results obtained. Differential diagnosis and medical care for children with gastroenterological pathology. |
|
Pediatric endocrinology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
Study of the organization of medical care for children in inpatient conditions. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, prevention of complications in children and adolescents with the most common diseases of the endocrine system. Study of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the endocrine system. Formation of knowledge and skills in laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of diseases of the endocrine system in children and interpretation of the results obtained. |
|
Pediatric nephrology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
Study of the organization of medical care for children in inpatient conditions. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, prevention of complications in children and adolescents with the most common nephrological diseases. Study of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment. Formation of knowledge and skills in the methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics and interpretation of the results obtained. Differential diagnosis and medical care for children with nephrological pathology. |
|
Pediatric Hematology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
Study of the organization of medical care for children in inpatient conditions. Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, prevention of complications in children and adolescents with the most common hematological diseases. Study of clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment. Formation of knowledge and skills in the methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics and interpretation of the results obtained. Differential diagnosis and medical care for children with hematological diseases. |
|
Neonatology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
The discipline provides knowledge and skills for providing medical care to a newborn in the delivery room, conducting clinical and laboratory-instrumental examinations with the interpretation of the results, differential diagnosis, choosing safe and effective management of newborns in the maternity hospital, predicting the outcome of the disease and conducting preventive measures, effectively interacting with the newborn’s parents and colleagues. |
|
Pediatric Neurology Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms knowledge, skills and abilities in the field of classification, etiopathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostics, basic principles of therapy for the most common neurological diseases in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine. |
|
Outpatient Pediatrics Number of credits – 8 Type of control – exam |
ДIsciplina forms knowledge and skills for the prevention of the most common infectious and non-communicable diseases in children, including the assessment of risk factors, methods of vaccination, personal and public hygiene, nutrition to maintain health and reduce mortality. |
|
Emergency medical care in pediatrics Number of credits – 3 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms knowledge and skills of diagnostics, differential diagnosis, emergency medical care for the most common emergencies conditions in children, taking into account age characteristics |
|
Paediatric infectious diseases Number of credits – 7 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms knowledge, skills and abilities related to the classification, etiopathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, basic principles of modern therapy of the most common infectious diseases in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine. |
|
Phthisiology for children Number of credits – 2 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms knowledge and skills in epidemiology, pathogenesis, modern methods of diagnosis, differential diagnosis, clinic, treatment and prevention of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis in children. |
|
Pediatric Surgery Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms the knowledge and skills of a pediatrician in the diagnosis, classification, etiopathogenesis, clinical manifestations, course and complications of the most common surgical diseases in children in the practice of a pediatrician, as well as the principles of conservative treatment and management of patients. |
|
Radiation diagnostic methods in the practice of a pediatrician Number of credits – 2 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms knowledge and skills in determining radiological symptoms and syndromes of the most common diseases of organs and systems in children, conducting differential radiological diagnostics, compiling an algorithm for radiological diagnostics based on risk assessment of radiological methods using the most effective of them in children |
|
Component of choice |
|
|
Patronage Follow-up of Young Children in Primary Health Care |
The discipline forms knowledge and skills in carrying out specific and non-specific prevention aimed at improving children’s health and reducing morbidity. The pediatrician carries out dynamic observation of children with disabilities, conducts a comprehensive assessment of the condition and rehabilitation measures to restore the child’s health and adaptation. |
|
Rehabilitation of children at the level of primary health care Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
A universally progressive model of patronage care for pregnant women and young children, developed by WHO and UNICEF, is being implemented in Kazakhstan within the framework of the Densaulyk program to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals. It is aimed at assessing medical and social risks, supporting the family, positive upbringing and promoting the health and well-being of children and parents. |
|
Assessment of ventilation function in children with respiratory tract diseases at the level of primary health care Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
Modern methods of functional diagnostics of the lungs in children make it possible to assess the main functions of the respiratory system. The most accessible and informative are spirometry and spirometry, the “gold standard” for assessing ventilation function and detecting bronchial obstruction. Peak flow metry is used to screen for breathing disorders. |
|
Electrocardiography in children Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a noninvasive method of assessing the electrical activity of the heart, used to diagnose and monitor heart disease in children. During the cycle, students master the taking and interpretation of ECG, differential diagnosis of cardiac pathologies and emergency conditions that require specialist consultation. |
|
Rare diseases in children Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
The elective is devoted to the topical problems of hereditary diseases in children. The training program, which includes modern management of a rare disease in children, provides the intern with the necessary knowledge and skills to provide medical care based on evidence-based medicine and modern pharmacotherapy. |
|
Pediatrics algorithms in the well-being of young children Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
The module forms students’ knowledge and skills in providing medical care to children 0–3 years old, diagnosing, treating and preventing diseases, and assessing the development of a child. Particular attention is paid to health promotion, family support, interdisciplinary interaction and prevention of diseases, injuries and developmental disorders. |
|
Neonatal Intensive Care Technologies Number of credits – 4 Type of control – exam |
The discipline forms the knowledge and basics of skills in providing medical care to a newborn in the delivery room, stabilizing the condition after birth, conducting clinical and laboratory-instrumental examinations with the interpretation of the results obtained, differential diagnosis, choosing safe and effective management of newborns in the maternity hospital, predicting the outcome of the disease and carrying out preventive measures, effective interaction with the parents of the newborn and colleagues. |
Name: General medicine Field of study: “Obstetrics and Gynecology”
Program code: 6B10107
Faculty: General medicine
The mission of the educational program
Formation of competitive healthcare specialists possessing professional competencies based on the integration of advanced educational, scientific, and medical technologies.
The purpose of the educational program:
Training specialists capable of providing qualified medical care to adolescent girls, pregnant women, women in labor, puerperas, women of reproductive and climacteric age; applying and developing advanced innovative technologies in practice and science; using information and communication technologies; promoting women’s health in outpatient and polyclinic settings and healthcare organizations located in rural areas, including district centers and urban-type settlements.
LO1 Apply medical, clinical, and epidemiological knowledge to solve clinical problems and improve patient health.
LO2 Provide high-quality medical care to pregnant women, women in labor, puerperas, and gynecological patients with the involvement of a multidisciplinary team in accordance with current evidence-based clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment.
LO3 Effectively interact with the patient, their environment, and healthcare professionals using communication skills to achieve the best outcomes for the patient.
LO4 Use the most effective methods of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention to ensure quality medical care.
LO5 Act within the legal and organizational framework of the healthcare system of the Republic of Kazakhstan according to one’s specialty, provide basic assistance in emergency situations, and work as part of interdisciplinary teams.
LO6 Formulate research questions, evaluate professional literature, effectively use international databases in everyday practice, and participate in research work.
LO7 Learn independently and actively participate in various forms of continuous professional development.
LO8 Analyze medical and statistical information, maintain medical documentation in accordance with legal requirements, and navigate and interpret computer-based patient information systems.
General education subjects
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline improves the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in outpatient and polyclinic settings in providing obstetric and gynecological care to adolescent girls, pregnant women, women in labor, postpartum women, and women of reproductive and climacteric age, in accordance with the clinical protocols of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan and evidence-based medicine.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The discipline enhances the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in managing physiological and complicated pregnancies, including those with concomitant extragenital pathology, according to clinical protocols of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan and evidence-based medicine; in providing emergency care to pregnant women.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in managing labor and the postpartum period in women with physiological childbirth, according to clinical protocols of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan and evidence-based medicine; in providing emergency care to women in labor and postpartum women, and in counseling on breastfeeding and contraception.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The discipline improves the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in managing labor and the postpartum period in women with concomitant extragenital pathology, according to clinical protocols of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan and evidence-based medicine; in providing emergency care to women in labor and postpartum women, and in counseling on breastfeeding and contraception.
Number of credits – 6
Type of control – Exam
The discipline aims to improve the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in providing qualified care to gynecological patients with uterine fibroids, endometriosis, benign ovarian formations, and uterine bleeding of unclear etiology.
Number of credits – 9
Type of control – Exam
The discipline enhances the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in modern principles of diagnosis and treatment of gynecological, precancerous, and malignant diseases of the female reproductive organs, and in the dispensary organization of oncological care, including screening methods.
Number of credits – 9
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops the knowledge and skills of an obstetrician-gynecologist in organizing qualified outpatient gynecological care for patients with recurrent pregnancy loss, infertility, and endocrine gynecological diseases, and in interpreting laboratory and instrumental test results for uterine and adnexal pathology.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline aims to form competencies in interns regarding the grounds and procedures for appointing and conducting forensic medical examinations, the rights, duties, and responsibilities of experts as regulated by the Criminal Procedure Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, and in providing qualified assistance to law enforcement officers.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline is aimed at familiarizing students with modern methods and technologies of invasive and non-invasive prenatal diagnostics for the timely detection of fetal congenital malformations, in order to prevent obstetric and perinatal complications, select optimal management tactics for pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, and prevent complications while preserving the woman’s reproductive function.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline is aimed at familiarizing students with modern methods and technologies in fetal surgery, including the use of fetal cells in medicine, for the timely diagnosis and prevention of obstetric and perinatal complications and gynecological diseases, as well as for choosing optimal management tactics during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, preventing complications, and preserving the woman’s reproductive function.
Name: General medicine Area of training “General medical practice”
Program code: 6B10107
Faculty: General medicine
The mission of the educational program
Of the educational program is aimed at the formation of competitive healthcare professionals with professional competencies based on the integration of advanced educational, scientific and medical technologies.
The purpose of the educational program:
Is to train a specialist – a general practitioner (family doctor) who knows the methods of diagnosis, treatment, prevention of the most common diseases in all age groups; early diagnosis of emergency conditions and provision of assistance in emergency conditions.
LO1 Engage in medical activities by applying knowledge of clinical and biomedical sciences in providing quality patient-centered treatment.
LO2 Interpret the results of clinical, laboratory and functional research methods at the stages of diagnosis and treatment of common diseases.
LO3 Understand public health issues, including prevention and public awareness of the munderstand public health issues, including prevention and public awareness of the most common diseasesost common diseases
LO4 Prescribe adequate treatment in accordance with the clinical situation; provide emergency medical care, including first aid and resuscitation.
LO5 Carry out the professional activities of a general practitioner taking into account the laws, regulations and ethical standards adopted in society.
LO6 Establish professional relationships with colleagues and the patient, work in a team to effectively perform professional tasks.
LO7 Apply IT technologies in the field of medicine to search for and critically analyze information and skills in medical information systems.
LO8 Apply scientific principles, methods, and knowledge of evidence-based practice to solve problems of clinical medicine and continuing professional development.
General education subjects
Number of credits – 12
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms the knowledge and skills of organizing care by a family doctor: screening, identification of risk factors, prevention (primary, secondary), therapy, outpatient rehabilitation, observation, education of patients and their relatives. Diagnosis, treatment, indications for consultation with specialists in common diseases in adults, adolescents, the elderly and pregnant women.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms knowledge and skills in diagnosing emergency surgical conditions (gastrointestinal tract, peritonitis, jaundice), examining injuries and diseases of the ODA in different age periods, conducting differential diagnosis, interpreting tests, making a diagnosis, prescribing treatment, providing emergency care and building professional relationships.
Module. General medical practice 1. Psychiatry and narcology at the level of primary health care
Number of credits – 2
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms knowledge on the organization of psychiatric and narcological care for primary health care, diagnostics and emergency care for depression, schizophrenia, neurosis, psychosis, addictions, gerontological disorders; teaches rehabilitation, expertise, timely referral of patients to specialized specialists.
Number of credits – 2
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms knowledge of syndromes of lesions of the central and peripheral nervous system. To apply knowledge in the organization of neurological care at the level of primary health care, the basic principles of therapy and the determination of indications for consultation with specialized specialists, timely detection and provision of emergency care for diseases of the nervous system
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
Discipline forms criteria for early diagnosis, principles of laboratory diagnostics, microbiological diagnostics, treatment, prevention, anti-epidemic measures in infectious diseases.
Number of credits – 2
Type of control – Exam
Methods of detection, diagnosis, and prevention of tuberculosis in children, adolescents, pregnant women and adults in primary health care.
Number of credits – 2
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms knowledge and skills on the principles of cancer alertness, early diagnosis, treatment, prevention and palliative care for cancer patients in accordance with modern clinical guidelines and principles of evidence-based medicine.
Number of credits – 12
Type of control – Exam
Organization of preventive and therapeutic and diagnostic care for children of different ages: antenatal prevention, vaccination, screening, identification of risk factors, observation. Diagnosis, treatment and differential diagnosis in accordance with clinical protocols. Determination of indications for consultation with specialized specialists in common childhood diseases.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms knowledge and skills to diagnose and manage pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period, interpret the results, prescribe treatment for obstetric and gynecological diseases, provide first aid, carry out prevention and information on gynecological and oncological diseases, apply evidence-based medicine and comply with the law.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
Fundamentals of Forensic Medicine for Medical Practice teaches physicians the basics of forensic science, injury assessment, cause of death, toxicology, and the legal aspects of working in the judicial system.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
ATC is the nomenclature of medicines. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs, their interaction. Indications, contraindications and side effects, Evidence-based medicine.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
Clinical and laboratory diagnostics in primary health care covers methods for diagnosing diseases based on clinical data and laboratory tests aimed at the effective provision of primary health care.
Name:General medicine the field of training «Therapy»
Program code: 6B10107
Faculty: General medicine
The mission of the educational program
Is aimed at developing competitive healthcare professionals with professional competencies based on the integration of advanced educational, scientific and medical technologies.
The purpose of the educational program:
Training of a qualified specialist doctor with a system of general cultural and professional competencies, able to independently carry out professional activities, mainly in conditions of primary health care in therapy, but also in conditions of emergency and specialized medical care.
LO1 To justify the choice of appropriate research methods from the standpoint of basic sciences, to carry out differential diagnosis, to use diagnostic criteria for the formulation and justification of the diagnosis.
LO2 To use the knowledge of rational pharmacotherapy in choosing safe and effective treatment (medicinal and non-medicinal) based on the principles of evidence-based medicine.
LO3 Diagnose and provide first aid for the most common life-threatening emergencies.
LO4 Apply the principles of epidemiology for the prevention and control of diseases, conduct medical check-up, health education, ensure infection control and participate in improving the health of patients and the population.
LO5 To draw up and maintain medical documentation, reflect timely and structured information about the patient’s health status.
LO6 Effectively interact with patients, their loved ones, colleagues and other healthcare professionals, showing empathy, taking into account individual characteristics, to ensure patient-oriented care.
LO7 To develop the ability to self-assess and analyze one’s own activities, set goals for continuous learning and self-improvement, eliminate gaps in knowledge and skills, as well as study independently and train others as part of a professional team, participate in discussions, conferences and other forms of continuous professional development.
LO8 Act within the legal and organizational framework of the healthcare system of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Number of credits – 6
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops knowledge and practical skills in managing adult patients with the most common diseases of bronchopulmonary pathology at the outpatient level, interpreting laboratory and instrumental methods, functional diagnostic methods, and managing dispensary patients according to the principles of bronchodilatory and antibacterial therapy, prevention, and rehabilitation, focusing on the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline builds knowledge and skills in diagnosis, interpretation of research results, treatment of patients with allergic diseases, and emergency care for life-threatening conditions, focusing on the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline enhances knowledge and practical skills in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, as well as emergency care in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops knowledge and skills in the diagnosis, interpretation of research results, and treatment of patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, focusing on the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline provides practical skills in diagnosing and treating common digestive diseases using modern methods, developing nutrition plans, providing emergency care and managing patients, including the postoperative and post-transplant period
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline enhances knowledge about the mechanisms of hematopoiesis and hemostasis, diagnostic skills and interpretation of laboratory and instrumental data, competence in the selection of drug and transfusion therapy, emergency care in critical conditions
Number of credits – 5
Type of control – Exam
This discipline provides the acquisition of knowledge and skills in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of endocrine diseases, as well as emergency medical care, based on the principles of evidence-based medicine and modern clinical guidelines
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline builds knowledge and skills for the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of the most common diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, focusing on the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 5
Type of control – Exam
The discipline forms the skills of early diagnosis, laboratory and microbiological research, as well as the skills of treatment, prevention and organization of anti-epidemic measures in infectious diseases
Module. Internal diseases-2. Phthisiology
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops knowledge and skills in the prevention, early detection, diagnosis, modern molecular genetic methods for the study of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis, emergency care (pulmonary hemorrhage and spontaneous pneumothorax), management of patients with comorbid pathology
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline develops knowledge and skills of topical diagnostics, selection of therapy, and emergency care for the most common neurological diseases based on the principles of evidence-based medicine
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline provides knowledge about the main diseases of endogenous and exogenous origin, risk factors for suicidal behavior, and management skills for patients with depression.
It enhances understanding of psychopharmacotherapy, interpretation of data from projective methods, neuropsychological testing, and self-administered questionnaires.
It cultivates the skills required for conducting an initial psychiatric interview and performing mental status examination
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline equips students with skills in interpreting ECG, Holter ECG, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), daily blood pressure monitoring (DBPM), and ankle–brachial index (ABI); identifying orthostatic hypotension; and mastering the basics of echocardiography (EchoCG) for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine and modern advances in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline is aimed at developing competencies in internal medicine interns for performing emergency procedures and practicing teamwork using high-technology simulation equipment, enabling the rehearsal of clinical scenarios in conditions that closely resemble real healthcare practice
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
The discipline focuses on developing interns’ competencies in understanding the principles, procedures, and conduct of forensic medical examinations, as well as the rights, duties, and responsibilities of experts regulated by the Criminal Procedure Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan. It also provides knowledge and skills for delivering qualified assistance to law enforcement authorities
Name: General medicine the field of training «Surgury»
Program code: 6B10107
Faculty: General medicine
The mission of the educational program
The mission of the educational program is aimed at developing competitive healthcare professionals with professional competencies based on the integration of advanced educational, scientific, and medical technologies.
The purpose of the educational program:
To train surgeons for the outpatient and polyclinic level of healthcare institutions in rural and district areas of the Republic of Kazakhstan, who possess professional skills in diagnosing acute surgical pathologies of the abdominal and thoracic organs, providing qualified medical assistance in cases of polytrauma, as well as treating primary and secondary purulent infections.
LO1 Apply biomedical, clinical, epidemiological, and socio-behavioral knowledge to solve surgical problems in adult patients and to improve their health
LO2 Provide qualified specialized care to adult patients with surgical diseases through a multidisciplinary team, in accordance with current clinical protocols for diagnosis and treatment based on evidence-based medicine
LO3 Effectively communicate with adult surgical patients, their families, and healthcare professionals, utilizing communication skills to achieve optimal treatment outcomes
LO4 Assess surgical risks and apply the most effective diagnostic, treatment, and preventive methods to ensure a high level of safety and quality of medical care for adult patients
LO5 Act within the legal and organizational framework of the healthcare system of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the specialty “Surgery (Adults)”, provide basic emergency care, and work in interprofessional teams to implement health promotion policies
LO6 Formulate appropriate research questions in the field of adult surgery, critically evaluate professional literature, effectively use international databases in daily practice, and participate in research activities
LO7 Demonstrate the ability for independent learning and active participation in various forms of continuous professional development in adult surgery
LO8 Analyze medical and statistical information, maintain medical documentation in accordance with regulatory requirements, and navigate and interpret patient data from computerized information systems in the field of adult surgery
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The module “Surgical Infections and Outpatient Surgery” is a key component in the training of a modern surgeon. It combines fundamental knowledge of infection control with skills in organizing and providing surgical care in innovative, more efficient formats. The module focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infectious processes encountered in surgical practice. Infection prevention is the cornerstone of successful outpatient surgery. The development of postoperative infectious complications automatically transfers a patient to inpatient care, negating the benefits of the outpatient approach. The module prepares surgeons to work under modern conditions that emphasize minimally invasive techniques, efficiency, and safety, with maximum use of outpatient facilities. It forms the basis for cost-effective and high-quality surgical care.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The main goal of the module is to train physicians to rapidly, accurately, and effectively diagnose and manage life-threatening conditions that require immediate or delayed surgical intervention. The core principle is: “First, save life — then treat the disease.”
The module is structured around syndromes and specific emergency conditions. “Emergency Surgery” is one of the most complex and responsible stages in surgical training. It demands not only excellent technical skills but also rapid decision-making, the ability to work under time and information constraints, and emotional resilience. Successful completion of the module signifies that the physician is ready to make life-critical decisions.
Practical skills developed in the module:
Emergency operations: laparotomy, thoracotomy (performed on mannequins, simulators, or in an operating room).
Minor surgical interventions:
Pleural puncture and drainage (thoracocentesis);
Bulau chest drainage for pneumothorax;
Pericardiocentesis;
Laparocentesis (diagnostic abdominal puncture);
Venous access (including central, in emergency cases);
Cricothyrotomy (emergency airway opening in upper airway obstruction).
Instrumental diagnostics: interpretation of X-rays, CT, and ultrasound in emergency conditions.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The module develops a systematic approach to the diagnosis and treatment of surgical diseases that do not require immediate intervention. The physician learns to plan and manage the entire process — from the patient’s initial consultation to discharge and rehabilitation.
The module also trains students to conduct full clinical examinations, practice the fundamentals of surgical techniques under non-urgent conditions, and make well-grounded decisions regarding the necessity and scope of surgical procedures.
Key objectives include:
Collecting complaints and medical history with an emphasis on the course of chronic diseases;
Performing physical examination of surgical patients (palpation,percussion, auscultation);
Assigning and interpreting routine investigations (laboratory tests, ultrasound, X-ray, CT, MRI, endoscopic methods — EGD, colonoscopy);
Formulating preliminary and clinical diagnoses;
Determining indications and contraindications for elective surgery;
Conducting preoperative preparation (correction of anemia, cardiac and pulmonary functions, etc.);
Acquiring basic surgical skills (postoperative management, suture removal, dressing techniques);
Managing medical documentation (case history, operation protocol writing).
Number of credits – 6
Type of control – Exam
The physician must possess fundamental knowledge of the diagnosis and management of common urological diseases, including urolithiasis, tumors, urinary tract infections, and congenital anomalies. The intern should be able to perform an initial examination, prescribe necessary investigations (ultrasound, laboratory tests), and carry out basic procedures such as catheter insertion. This module combines both conservative and surgical approaches, making it highly versatile and practically oriented.
The goal of the module is to provide interns with systematic knowledge and practical skills for diagnosing and managing the most common urological conditions.
Upon completion, the intern should be able to:
Recognize typical urological symptoms;
Perform an initial assessment of a urological patient;
Provide emergency care for urological emergencies;
Understand the principles of elective and surgical treatment.
The “Urology” module provides interns with fundamental competencies valuable in any medical specialty. The ability to diagnose renal colic, manage acute urinary retention, or suspect a neoplasm are essential skills for every physician. For those interested in this field, the module serves as the first step toward a urology career. Successful completion demonstrates that the intern is confident in identifying urological symptoms and can competently act in both outpatient and inpatient settings.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – Exam
The goal of this discipline is to train interns to diagnose and provide primary care for injuries and diseases of bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles. The physician must understand the distinction between emergency conditions (e.g., open fractures) and chronic diseases (e.g., coxarthrosis).
The “Traumatology and Orthopedics” module represents a unique specialty at the intersection of surgery, internal medicine, and rehabilitation. For the intern, it provides an excellent opportunity to develop clinical reasoning skills (analyzing the mechanism of injury and predicting possible damage) and to acquire valuable manual experience.
Key learning objectives:
Diagnosis: ability to establish a diagnosis (type of fracture or dislocation) based on examination and X-ray data.
Emergency care: immobilization, pain management, and prevention of shock.
Mastery of basic conservative treatment methods: plaster immobilization, skeletal traction. Assisting in surgical operations. Postoperative management and basics of rehabilitation.
Number of credits – 7
Type of control – Exam
The “Thoracic Surgery” module aims to provide surgical interns with fundamental knowledge of the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic diseases. Its primary objective is to train interns to deliver emergency care in thoracic emergencies and to understand the principles of this high-technology surgical specialty.
Key learning objectives:
Master the symptomatology of thoracic diseases (cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea, chest pain).
Learn to interpret chest X-rays and CT scans (identify pneumothorax, hemothorax, atelectasis, pleural effusion).
Acquire practical skills in emergency management of life-threatening conditions (tension pneumothorax, hemothorax, cardiac tamponade).
Understand and perform pleural drainage techniques (thoracentesis, Bülau drainage).
Assist in elective and emergency thoracic operations.
Number of credits – 7
Type of control – Exam
The “Ophthalmology and Otorhinolaryngology” module aims to train surgical interns in the recognition and emergency management of eye and ENT (ear, nose, throat) conditions that require immediate medical attention. Delayed or incorrect diagnosis in these areas may lead to severe complications such as blindness, airway obstruction, or life-threatening outcomes.
Main objectives:
Ophthalmology:
– Identify vision-threatening conditions (eye trauma, foreign bodies, contusions).
– Provide first aid for ocular injuries, corneal foreign bodies, and hyphema.
– Follow proper management protocols for suspected penetrating eye injuries (protective eye dressing, no pressure, urgent ophthalmology referral).
Otorhinolaryngology:
– Diagnose and manage emergency conditions involving the ear, nose, and throat (airway obstruction, epistaxis, foreign bodies).
– Understand stabilization algorithms and emergency interventions for ENT-related emergencies.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
This course aims to develop interns’ competencies in the field of forensic medical examination. It covers the legal framework, procedures for appointing and conducting forensic medical evaluations, and the rights, duties, and responsibilities of experts as regulated by the Criminal Procedure Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The discipline also focuses on building practical skills for effective collaboration with law enforcement authorities in medico-legal investigations.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
This course covers the causes and mechanisms of cerebrovascular disorders, modern diagnostic techniques, indications for surgical intervention, types of operative procedures, and principles of postoperative management. Emphasis is placed on complication prevention and improving patient outcomes.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – Exam
This discipline focuses on identifying sources and transmission routes of infections, developing and implementing preventive measures against HAIs, monitoring compliance with aseptic and antiseptic standards, promoting rational antibiotic use, and improving patient safety in surgical settings.
Mission of the educational program – development of professional competencies and personal qualities in interns to prepare competitive specialists with theoretical knowledge and practical skills for effective professional activity in the treatment of surgical diseases in children.
RO1. Apply knowledge of clinical and biomedical sciences to ensure high-quality, patient-centered care for children with surgical pathology. Perform differential diagnosis and formulate diagnoses considering modern classifications.
RO2. Organize and provide medical care to children in outpatient and polyclinic settings. Apply skills in planning, conducting, and analyzing clinical, laboratory, and instrumental examinations in patients.
RO3. Select safe and effective treatments based on the principles of evidence-based medicine considering potential risks. Determine indications and provide qualified assistance in urgent and life-threatening conditions.
RO4. Assess therapy effectiveness based on evidence-based practice, predict disease outcomes and complications, conduct preventive and rehabilitation activities.
RO5. Maintain and manage medical records and reporting documentation, including in medical information systems.
RO6. Act within the legal and organizational framework of the healthcare system of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
RO7. Effectively communicate with patients, their families, and colleagues within multidisciplinary teams to achieve the best outcomes for patients.
RO8. Apply scientific approaches, methods, and the principles of evidence-based medicine in clinical practice and for continuous professional development.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – exam
Forms knowledge and skills for conducting preliminary diagnostics, determining treatment tactics, and providing urgent primary care to children with common diseases, congenital anomalies, traumatic injuries, and emergencies in outpatient and polyclinic settings.
Number of credits – 9
Type of control – exam
Develops universal and professional competencies in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of urgent conditions and in providing emergency surgical care to children; builds teamwork and communication in inter-professional settings.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – exam
Develops skills in performing detailed clinical examinations, interpreting laboratory and instrumental findings, performing differential diagnosis per accepted classifications, and selecting effective pathogenetic treatment of suppurative-inflammatory surgical diseases.
Number of credits – 9
Type of control – exam
Provides knowledge and skills in using advanced diagnostic and treatment methods for surgical diseases of the abdominal organs (portal hypertension, hepatobiliary anomalies, pancreatic and GI diseases, parasitic liver diseases, etc.), effectively using international databases in daily practice.
Number of credits – 5
Type of control – exam
Builds competence in planning and conducting clinical, laboratory, and instrumental examinations, performing differential diagnosis per modern classifications, interacting effectively with patients and colleagues, and using international databases in practice.
Number of credits – 8
Type of control – exam
Develops universal knowledge and professional skills in diagnosing musculoskeletal, CNS, abdominal, and urogenital injuries; determining indications and contraindications for surgical treatment; and coordinating multidisciplinary teamwork.
Number of credits – 5
Type of control – exam
Develops competencies in performing detailed examination of newborns, interpreting diagnostic tests, performing differential diagnosis and formulating final diagnoses, and selecting surgical methods for congenital malformations of the thorax, abdomen, anorectal region, urinary tract, and anterior abdominal wall.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
The discipline forms knowledge and skills in carrying out specific and non-specific prevention aimed at improving children’s health and reducing morbidity. The pediatrician carries out dynamic observation of children with disabilities, conducts a comprehensive assessment of the condition and rehabilitation measures to restore the child’s health and adaptation.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
A universally progressive model of patronage care for pregnant women and young children, developed by WHO and UNICEF, is being implemented in Kazakhstan within the framework of the Densaulyk program to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals. It is aimed at assessing medical and social risks, supporting the family, positive upbringing, and promoting the health and well-being of children and parents.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
Modern methods of functional diagnostics of the lungs in children make it possible to assess the main functions of the respiratory system. The most accessible and informative are spirometry and spirometry, the “gold standard” for assessing ventilation function and detecting bronchial obstruction. Peak flowmetry is used to screen for breathing disorders.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a noninvasive method of assessing the electrical activity of the heart, used to diagnose and monitor heart disease in children. During the cycle, students master the taking and interpretation of ECG, differential diagnosis of cardiac pathologies and emergency conditions that require specialist consultation.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
The elective is devoted to the topical problems of hereditary diseases in children. The training program, which includes modern management of a rare disease in children, provides the intern with the necessary knowledge and skills to provide medical care based on evidence-based medicine and modern pharmacotherapy.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
The module forms students’ knowledge and skills in providing medical care to children 0–3 years old, diagnosing, treating and preventing diseases, and assessing the development of a child. Particular attention is paid to health promotion, family support, interdisciplinary interaction, and prevention of diseases, injuries, and developmental disorders.
Number of credits – 4
Type of control – exam
The discipline forms the knowledge and basics of skills in providing medical care to a newborn in the delivery room, stabilizing the condition after birth, conducting clinical and laboratory-instrumental examinations with the interpretation of the results obtained, differential diagnosis, choosing safe and effective management of newborns in the maternity hospital, predicting the outcome of the disease and carrying out preventive measures, effective interaction with the parents of the newborn and colleagues.